对象和定制属性
对象和自定义属性
通过定义对象的自定义属性,可以完成业务上需要的特殊处理,例如:定义对象的id或value等等,以方便后续的逻辑处理。
自定义属性
在构建应用程序时,你可能需要向对象添加一些自定义属性。一个非常常见的需求是将id和name属性添加到对象上。
如果你正在使用 TypeScript 或者希望你的IDE能够提供自动补全功能,那么你需要明确声明这些属性是什么。
此外,还存在一个序列化的问题,需要你在函数toObject的参数中传递这些属性。
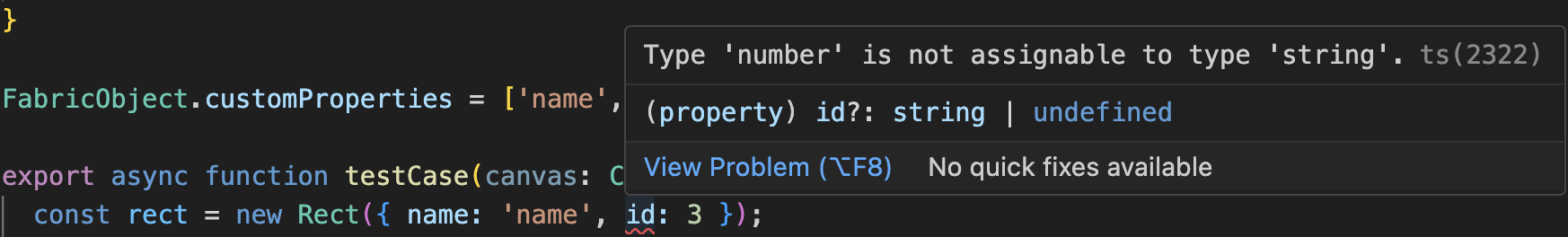
// 直接用,但没有ts的提示检测:(myRect as any).name = 'rectangle';myRect.toObject(['name', 'id']);为了使代码更美观,你必须使用 TypeScript 的接口特性和对象的自定义属性钩子。
import { FabricObject } from 'fabric';
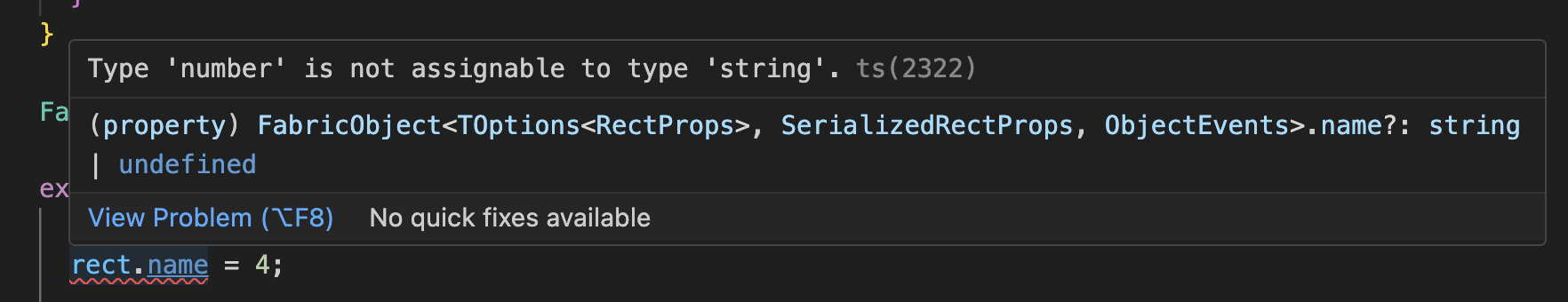
declare module "fabric" { // 确保类的属性不仅在实例对象中可以访问和使用,而且也能在构造函数中被正确识别和初始化 interface FabricObject { id?: string; name?: string; } // 确保导出的对象具有类型化的属性 interface SerializedObjectProps { id?: string; name?: string; }}
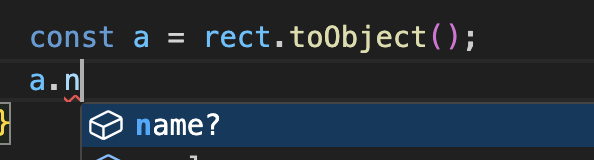
// 确保属性实际添加到序列化对象中FabricObject.customProperties = ['name', 'id'];这样的改变将使类型推断工作正确:
- 错误1
- 错误2
- 正确
自定义方法
一般来说,如果你能坚持使用外部函数,事情会变得简单。但在特定情况下,当你想将特定的方法添加到不同对象的原型上时,你必须进行一些修改:
// declare the methods for typescriptdeclare module "fabric" { // to have the properties recognized on the instance and in the constructor interface Rect { getText: () => string; } // to have the properties typed in the exported object interface Text { getText: () => string; }}
// then add the methods to the classes:Rect.prototype.getText = function() { return 'none'; }Text.prototype.getText = function() { return this.text; }定义子类
定义子类变得更加容易,但并不总是可行的。例如,如果你想定义像Rect, Textbox, IText, Path的派生类,这是可能且容易的。
import { classRegistry, SerializedPathProps } from 'fabric';
interface UniquePathPlusProps { id?: string; name?: string;}
export interface SerializedPathPlusProps extends SerializedPathProps, UniquePathPlusProps {}
export interface PathPlusProps extends SerializedPathProps, UniqueRectProps {}
export class PathPlus< Props extends TOptions<PathPlusProps> = Partial<PathPlusProps>, SProps extends SerializedPathPlusProps = SerializedPathPlusProps, EventSpec extends ObjectEvents = ObjectEvents,> extend Path<Props, SProps, EventSpec> { static type: 'path' // 如果你希望它完全覆盖 Path declare id?: string; declare name?: string;
toObject< T extends Omit<Props & TClassProperties<this>, keyof SProps>, K extends keyof T = never, >(propertiesToInclude: K[] = []): Pick<T, K> & SProps { return super.toObject([...propertiesToInclude, 'id', 'name']); }}
// 使得从序列化数据中恢复成为可能classRegistry.setClass(PathPlus, 'path');// 使 PathPlus 与 SVG Path 元素关联classRegistry.setSVGClass(PathPlus, 'path');但是,你不能派生一个FabricObject并将其添加到其他对象的原型链中。